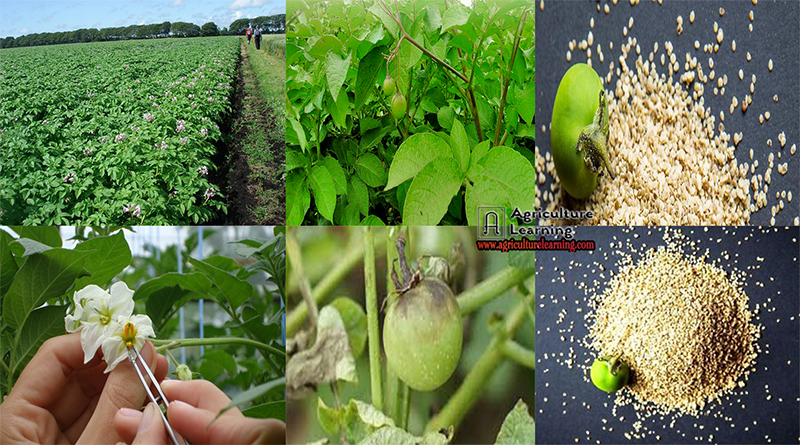
True Potato seed (TPS) production technique and it’s advantages
True Potato seed (TPS) is the actual botanical seed produced by the sexual reproduction and is formed inside the fruits/berries, resembling tomatoes. TPS is occasionally formed after the potato has finished flowering.
True potato seed is very effective and cheap source of planting material. The shortage of good quality seed tubers, high cost of seed, transportation problem, virus infiltration in seed tubers are some of the problems associated with the use of seed tubers as planting material. The concept of raising potato crop from true potato seed (TPS) or botanical seed was conceived in India in the early fifties by Dr. S. Ramanujan, the founder director of CPRI.
Paired-row concept for Cultivation of True Potato Seed:
Paired-row concept for Cultivation of True Potato Seed (TPS) is the innovation in which TPS are sown in narrow inter space of 10 cm 10 cm with 5 cm for plant to plant distance. A total of 100 plants per m2 where maintained in all class.
This innovation is less laborious than a single row system, which need more time. Very high level of seedling maintenance is the major utility of this concept.
Selection of parents: Selection of parents is based on quantity of hybrid TPS, which can be produced from per unit area from heterosis. Generally, clones of S. tuberosum are used as female and S. andigena as male that result in heterosis with added advantage of high pollen load.
Planting of parents:
- Cut pieces of tuber obtained from male and female plants are planted in separate blocks with required staggering period i.e. 7 days early planting of male than the female to facilitate pollen availability.
- Recommended planting geometry for male is 6020 cm an 5015 cm for female.
- The block with tuber of female parent is kept 1 m wide with a walking space of 80 cm between blocks.
Light Requirement:
Potato plant require large photoperiodic condition for flowering. In plains flowering can be achieved by providing 5 hour of extra illumination during flowering i.e. December-January from 4 to 9 pm with sodium vapour lamp of 150 watt. One sodium bulb is sufficient to cover an area of 100 sqm.
Pollination and fertilization:
- To minimize duration of pollination, bud and flower bunches are trimmed to remain 6 buds/branch.
- The mature male flowers are collected in the evening and stored over night at room temperature for higher recovery of pollens.
- In commercial seed production program pollination is done 2-3 times at interval of 8 hour without emasculation to save the time.
- It allows 1-5% selfing.
Harvesting and processing:
- Berries are picked after 45-50 days of pollination and allow to ripen. A hand operated reverse screw juice extractor is used to extract the seed.
- The seed and pulp are treated with 10% HCL with continuous stirring for 20 minutes. The debris is removed by nylon net of 3.13 mm mesh size.
- The seed is washed 3-4 times with water for complete removal of HCL.
- Seeds is spread over a thin layer and dried under shade for 72 hour and exposed to sunlight for 30 minutes so that the moisture content up to 5-7% is maintained.
Packaging and storage:
The seed is packed in double layer polythene bags and stored at room temperature for short-term storage and at 6-10-degree calcius for long term storage.
Seed sowing:
- Freshly harvested TPS have dormancy of approximate 180 day therefore, storage for at least a year is recommended.
- Dormancy can be released by soaking the seed in 1500-2000 ppm GA3 solution for 48 hours.
- In heavy soil, TPS can be sown directly.
Advantage of using True potato seeds as planting material:
- TPS is cheaper (nearly 1/10 cost of seed tubers) and affordable for small and marginal farmers.
- 100 grams is sufficient to cover one hectare instead of planting 2.5-3.0 tons of potato seed tuber.
- TPS is a healthy and disease-free planting material.
- TPS has capability of giving more production.
- No cold storage facility is required for storing TPS
- Comparatively more resistance to pests and diseases.
- Net profit is more as cost of cultivation is less and also as per hectare production is much more.
- The seed tubers being utilized could be otherwise used for consumption.
- Total cost of potato production using TPS is nearly half that of tubers with equivalent yield.
Disadvantages of Conventional TPS:
- TPS-raised crops raised are not uniform in various parameters such as emergence, plant type, tuber traits (shape, size and color) and crop maturity, and differ compared to tuber-raised crops.
- TPS crop is more labor-intensive especially during seedling raising, transplanting, and further establishment of the commercial crop.
- TPS has a long natural dormancy period of up to one year, and therefore dormancy of fresh seeds is broken with hormonal (GA3) treatment.